Problem 5: Towers of Hanoi (100pts)
A classic puzzle called the Towers of Hanoi is a game that consists of three rods, and a number of disks of different sizes which can slide onto any rod. The puzzle starts with n disks in a neat stack in ascending order of size on a start rod, the smallest at the top, forming a conical shape.
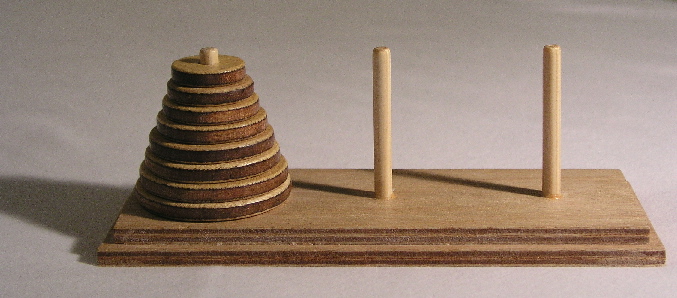
The objective of the puzzle is to move the entire stack to an end rod, obeying the following rules:
- Only one disk may be moved at a time.
- Each move consists of taking the top (smallest) disk from one of the rods and sliding it onto another rod, on top of the other disks that may already be present on that rod.
- No disk may be placed on top of a smaller disk.
Complete the definition of move_stack, which prints out the steps required to move n disks from the start rod to the end rod without violating the rules. The provided print_move function will print out the step to move a single disk from the given origin to the given destination.
Hint: Draw out a few games with various
non a piece of paper and try to find a pattern of disk movements that applies to anyn. In your solution, take the recursive leap of faith whenever you need to move any amount of disks less thannfrom one rod to another. If you need more help, see the following hints.
Extra hints
- Hint1: See the animation of the Towers of Hanoi, found on Wikimedia by user Trixx
- Hint2: The strategy used in Towers of Hanoi is to move all but the bottom disc to the second peg, then moving the bottom disc to the third peg, then moving all but the second disc from the second to the third peg.
- Hint3: One thing you don't need to worry about is collecting all the steps.
def print_move(origin, destination):
"""Print instructions to move a disk."""
print("Move the top disk from rod", origin, "to rod", destination)
def move_stack(n, start, end):
"""Print the moves required to move n disks on the start pole to the end
pole without violating the rules of Towers of Hanoi.
n -- number of disks
start -- a pole position, either 1, 2, or 3
end -- a pole position, either 1, 2, or 3
There are exactly three poles, and start and end must be different. Assume
that the start pole has at least n disks of increasing size, and the end
pole is either empty or has a top disk larger than the top n start disks.
>>> move_stack(1, 1, 3)
Move the top disk from rod 1 to rod 3
>>> move_stack(2, 1, 3)
Move the top disk from rod 1 to rod 2
Move the top disk from rod 1 to rod 3
Move the top disk from rod 2 to rod 3
>>> move_stack(3, 1, 3)
Move the top disk from rod 1 to rod 3
Move the top disk from rod 1 to rod 2
Move the top disk from rod 3 to rod 2
Move the top disk from rod 1 to rod 3
Move the top disk from rod 2 to rod 1
Move the top disk from rod 2 to rod 3
Move the top disk from rod 1 to rod 3
"""
assert 1 <= start <= 3 and 1 <= end <= 3 and start != end, "Bad start/end"
"*** YOUR CODE HERE ***"